Anti-VEGF Bevacizumab (Avastin®) Found Helpful for Radiation Optic Neurology
In an interventional case study from the New York Eye Cancer Center, evaluated intravitreal bevacizumab treatment for radiation optic neuropathy (RON).
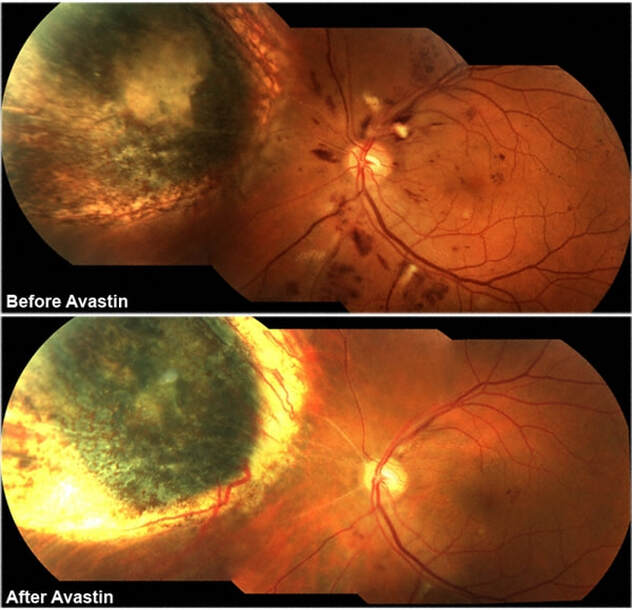
A patient symptomatic of decreased vision because of RON was treated with intravitreal bevacizumab (1.25 mg) over several 6-8 week cycles. Main outcome measures included visual acuity, appearance of the optic nerve, fundus photography, angiography and optical coherence tomography/scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (OCT/SLO).
Within one week, her vision improved from 20/32 to 20/20 with a reduction in optic disc hemorrhage. At six weeks, both decreased hemorrhage and optic disc edema were documented by photography, angiography and OCT/SLO. At her 3 and 5 month follow-up visits, the hemorrhages resolved, the patient’s disc margins were sharp and her vision was stable at 20/20. No ocular or systemic side effects were noted.
In conclusion, intravitreal bevacizumab was tolerated, improved vision and reduced hemorrhage and optic disc edema. Based on results of this case report, the author recommended that Anti-VEGF therapy (e.g., bevacizumab) should be investigated for ocular and nonocular radiation neuropathy.
Finger PT. Anti-VEGF bevacizumab (Avastin) for radiation optic neuropathy.
American Journal of Ophthalmology 2007;143(2):335-8.
Related Links
Read the abstract as printed online in the American Journal of Ophthalmology
Read the abstract as it appears in PubMed
Receive the latest news and opportunities from The Eye Cancer Foundation. Please fill out the form below.
A patient symptomatic of decreased vision because of RON was treated with intravitreal bevacizumab (1.25 mg) over several 6-8 week cycles. Main outcome measures included visual acuity, appearance of the optic nerve, fundus photography, angiography and optical coherence tomography/scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (OCT/SLO).
Within one week, her vision improved from 20/32 to 20/20 with a reduction in optic disc hemorrhage. At six weeks, both decreased hemorrhage and optic disc edema were documented by photography, angiography and OCT/SLO. At her 3 and 5 month follow-up visits, the hemorrhages resolved, the patient’s disc margins were sharp and her vision was stable at 20/20. No ocular or systemic side effects were noted.
In conclusion, intravitreal bevacizumab was tolerated, improved vision and reduced hemorrhage and optic disc edema. Based on results of this case report, the author recommended that Anti-VEGF therapy (e.g., bevacizumab) should be investigated for ocular and nonocular radiation neuropathy.
Finger PT. Anti-VEGF bevacizumab (Avastin) for radiation optic neuropathy.
American Journal of Ophthalmology 2007;143(2):335-8.
Related Links
Read the abstract as printed online in the American Journal of Ophthalmology
Read the abstract as it appears in PubMed
Receive the latest news and opportunities from The Eye Cancer Foundation. Please fill out the form below.